
Safeguarding critical infrastructure sectors like energy, water, and transportation is vital for public health, safety, and economic stability. The North American Electric Reliability Corporation’s (NERC) Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) standards provide a cybersecurity framework specifically designed to protect these vital assets.
As threats evolve, both awareness and ongoing compliance with NERC CIP are essential for organizations in regulated critical infrastructure industries. This article explores the significance, requirements, challenges, and future trends associated with NERC CIP standards.
What Are The Rules To Keep The Power Grid Safe?
Ensuring the reliable delivery of electricity across the country is of utmost importance. Power companies must follow security rules called NERC CIP to protect critical equipment from getting hacked or damaged. This guide explains the main NERC rules in easy-to-understand language. Having a grasp of the basics helps keep everyone’s lights on!
Challenges And Common Pitfalls In NERC CIP Implementation
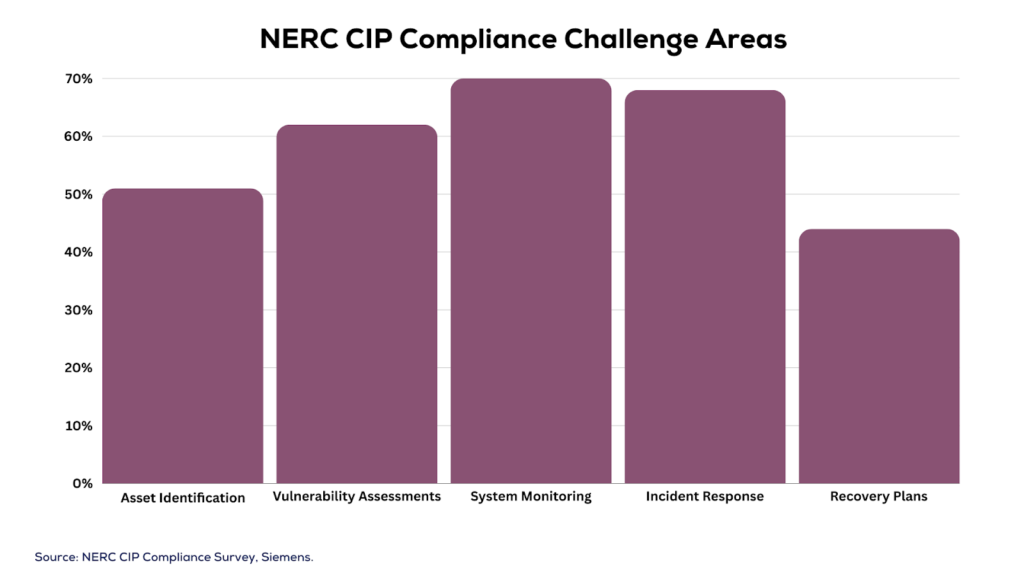
Despite stringent standards, many entities struggle on the road to NERC CIP compliance. A survey revealed challenges related to monitoring (72% of respondents), incident response (68%), and access control (66%) (SANS Institute, 2020).
Difficulties arise from the complexity of legacy hardware, inadequate resources, supply chain risks, and lack of cybersecurity maturity. Strategic planning, executive buy-in, comprehensive staff training, and security technology investments can help overcome hurdles.
What Is NERC
NERC stands for the North American Electric Reliability Corporation. Their job is to set reliability rules that help prevent blackouts and keep power systems secure in the United States, Canada, and parts of Mexico. NERC creates standards and guidelines called Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) that companies that make or deliver electricity must obey.
The rules help those companies better spot risks, guard against cyber security issues like hacking, get prepared for bad events, and keep their technology working properly. NERC guides companies on critical things like identifying important equipment, reducing the danger from storms or attacks, responding quicker to problems, and sharing data to boost safety.
By requiring companies to follow its defense guidelines through CIP rules and related frameworks, NERC helps strengthen protections for crucial electrical systems. This guards the reliability of power flowing to homes, businesses, hospitals, and more so our economy and lives aren’t disrupted. NERC remains committed to constantly updating its standards as technology changes to keep communities secure.
What Is The CIP Program
CIP means Critical Infrastructure Protection. This NERC program tells power companies exactly what they need to do to safeguard important gear that keeps electricity flowing. There are currently 8 CIP rules, each covering an area like cybersecurity, employee training, and managing risks. Power firms must prove to NERC that they are following all guidelines.
Why Did NERC Create The CIP Rules
In 2003 over 50 million people lost power across parts of the U.S. and Canada! The big power outage was caused by overgrown trees hitting power lines and buggy monitoring software. NERC made CIP to prevent dangerous future blackouts by protecting key parts like power plants, substations, and control centers. Security issues can also cause outages which CIP helps prevent.
What’s Covered Under CIP
The CIP rules apply to bulk electric systems – the big high power lines, transformers, and generation stations that move electricity nationwide. Smaller local utility companies that deliver energy to homes and businesses don’t have to follow most CIP requirements. NERC focuses protection on the very heavy-duty backbone equipment of the whole system.
CIP-002 – What’s Critical
The first rule CIP-002 says power companies must inventory their “critical cyber assets”. Any computer gear that runs programs controlling how electricity flows needs extra precautions like login passwords. Critical cyber assets get special handling and monitoring laid out in the other CIP rules. Identifying this cyber gear is job #1!
CIP-003 – Securing Those Assets
Once critical cyber systems are identified, CIP-003 requires power firms to document detailed security plans. These plans must list exactly how critical computers and programs will be protected from hackers, viruses, or anyone tampering by mistake. There should be no room for guesswork; written procedures are essential to ensure that employees know how to safeguard critical control equipment.
CIP-004 – Managing Access
The companies also need to list all staff with any critical systems access under CIP-004 and have processes so permissions get changed promptly if a worker leaves their job. No loosey-goosey access – strict tracking of who can get into the crucial control networks and software must be documented. No system login sharing allowed!
Cip-005 And 006 – System Safeguards
These two standards cover building protections such as fences, alarms, security officers, and video cameras for facilities housing important computers, programs, and power management equipment. Safety measures must appear across all sites to detect issues quickly. Ruined fences and broken cameras mean fines!
CIP-007 – Addressing Issues Quickly
If a cyber security problem pops up with critical equipment, CIP-007 requires processes detailing how firms will respond promptly. Everyone needs assigned roles detailing who leads investigations, who makes fixes, who restore backups, and how to keep executives informed on what’s happening. Fast reaction to incidents helps avoid lengthy blackouts.
Cip-008 And 009 – Being Ready For Problems
The final CIP standards require companies to prepare for outages and cyberattacks. They need emergency response strategies to map everything out ahead of time. Think of them as safety drills for grid incidents, much like fire drills for fire safety. Companies must also back up and secure critical IT blueprints, along with spare parts, in case rebuilding becomes necessary.
Staying Compliant With CIP
As you can see, NERC’s CIP rules are thorough but make tons of sense. Following the guidelines helps prevent future massive blackouts. Power companies must prove full compliance by undergoing regular NERC audits. New standards come out periodically too so keeping up-to-date stays important. But when critical infrastructure has oversight and smart protection, communities across North America benefit!
FAQs
What are the key NERC CIP standards, and how do they apply to different sectors within critical infrastructure?
The main standards focus on identifying critical cyber assets, security management, electronic/physical security perimeters, incident handling, recovery plans, and supply chain protections. Their implementation varies based on specific critical infrastructure subsectors like energy, dams, transportation, and water.
What are the penalties for non-compliance, and how can organizations avoid them?
Violations carry severe annual financial penalties in addition to mandated remediation costs, exceeding $1 million in some cases. Robust internal controls for compliance program management, change control processes, and cybersecurity enable avoiding violations.
How can organizations stay updated on the latest NERC CIP developments?
Routinely reviewing standards at www.nerc.com, participating in industry working groups, attending NERC conferences, leveraging compliance bulletins, and monitoring enforcement actions ensure organizations adjust cybersecurity strategies for evolving standards.
Final Thoughts
As threats targeting critical infrastructure continue intensifying, NERC CIP regulations will serve as the bulwark safeguarding the essential services vital for daily life. Maintaining awareness and compliance with these comprehensive protections now can prevent untold disruption tomorrow.
Read Also:




























