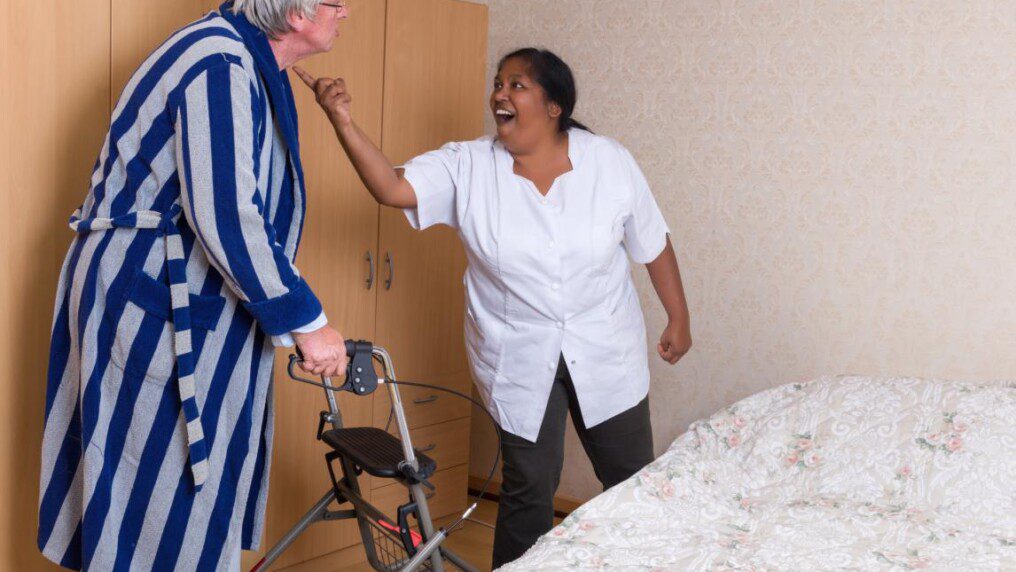
Age should be a time of dignity, comfort, and respect-a period in life when elders are cared for and treasured.
The sad reality, however, is different: abuse, neglect, or exploitation of millions of elderly persons around the world often comes from those closest to them.
Much of the abuse goes on behind closed doors and unreported; learning what to look for and how to act can make all the difference.
This article will outline signs of elder abuse, types and causes, consequences, and what you can do to prevent or report it.
What is Elder Abuse?
Abuse of older adults may be defined as any willful or negligent act or inaction by the caregiver of an older adult which causes harm or distress to the older adult. It may also occur in a private home, nursing facility, hospital, or community setting.
This is a serious violation of human rights and can be manifested through physical hurt, emotional ill-treatment, financial exploitation, or neglect.
Unfortunately, most of the victims go through their pain in silence due to fear, shame, or dependence on their abusers.
What is the Type of Elder Abuse?
Abuse of elders takes many forms and most situations involve more than one type. The first step toward protection of a vulnerable senior starts with an awareness of those forms.
1. Physical Abuse
Physical abuse is defined as the utilization of physical force that could result in bodily injury, pain, or physical impairment. It includes acts of hitting, slapping, pushing, shaking, or inappropriate restraint of an elderly individual.
Warning signs include but are not limited to unexplained bruises, burns, fractures, dislocated joints, or repeated “accidents”. Other kinds of abuse include fear of caretakers or withdrawal from physical contact.
2. Sexual Abuse
Sexual abuse is any sexual contact with an elderly individual that is performed without the elder’s consent.
It includes anything from unwanted touching to rape and can occur regardless of whether the victim is cognitively impaired or not.
These include bruising or bleeding in the genital area, torn or stained underwear, unexplained infections, and changes in behavior such as fearfulness or avoidance of certain individuals.
3. Neglect
Neglect involves the failure of caretakers to provide necessary care that results in either injury or distress. It also encompasses the failure to provide nutrition, hygiene, medical care, or an appropriate living environment.
This also involves signs that show malnutrition, dehydration, unmet medical needs, poor personal hygiene, bed sores, and an unkempt/unattended appearance.
4. Financial Abuse
Financial or material exploitation is an act that involves using the funds, property, or any other assets belonging to an elder in a manner that is either unlawful or improper. It is one of the more common, yet harder-to-detect forms of abuse against older people.
Examples of such exploitation include theft, misuse of bank accounts, forcing an older person to sign documents, scams, or sudden changes to wills and powers of attorney.
Warning signs include unexplained withdrawals, bills not paid, missing possessions, and sudden financial changes that are suspect.
5. Emotional Abuse
Psychological or emotional abuse can be both verbal and non-verbal. It may encompass any act that causes a person to feel anguish, fear, or distress. It is equivalently injurious as physical violence.
Examples of emotional abuse include: yelling, intimidation, humiliation, isolation, or treating the elder like a child.
These may include symptoms such as depression, withdrawal, anxiety, agitation, low self-esteem, or unusual behaviors like rocking and mumbling.
6. Abandonment
Abandonment means a situation whereby a caregiver has stopped providing support necessary for the elderly person, either in places such as hospitals, public places, or at home.
Examples include abandoning or leaving an older person unattended without access to resources, and when he shows up in unfamiliar surroundings lost, confused, and disoriented.
Who Is At Risk For Elder Abuse?
The following factors increase the risk for abuse:
- Advanced age or physical frailty
- Social isolation or living alone
- Dependent on caregivers for daily needs
They include:
- Substance abuse or mental health problems of the caregiver
- Financial dependence of the abuser on the elder
- Is it ever too late to have your breakfast? No!
How Common is Elder Abuse?
Elder abuse is more common than most people would ever imagine. According to estimates made by the WHO, about 1 in 6 older adults in the world experiences some type of abuse in any given year.
Experts, however, believe that for every case reported, as many as 24 cases go unreported, often because the victims fear retaliation or losing their caregivers.
Elder abuse is an issue best approached through awareness and vigilance since the reality of the problem often hides behind a screen of silence and stigma.
What Does Elder Abuse Do?
The consequences of elder abuse are dire: physical, emotional, and financial. Long-term trauma, deteriorating health, loss of trust, and even premature death may result.
The victims may become fearful, depressed, or withdrawn; many of them suffer silently because they are dependent upon their abuser.
It financially wipes out the life savings, destroys years of planning, and makes elders helpless. The betrayal of loved ones inflicts deep and often irreparable psychological injury on an emotional plane.
It is at this surface that reflected waves are combined with those that have passed directly through to reconstruct the original sound.
What are the Signs of Elder Abuse?
There are a few signs of elder abuse that you need to look into to fully understand these as signs. So a few of these common signs include:
- Sudden mood swings, fearful or withdrawn
- Poor hygiene, dirty clothes, or malnutrition
- Isolation with caregivers refusing to allow visitors
- Sudden changes in wills, deeds, or other financial documents
- Overmedication or no medication at all.
Watch for signs of anxiety, depression, or confusion. Trust your instincts. When one thing feels “off, it is worth investigating.
In other words, it is not sufficient to protect life, but it has to be so preserved that there is advance and progress from generation to generation.
What Are the Consequences of Elder Abuse?
The ramifications of elder abuse go beyond direct harm. Physical consequences include injury, chronic pain, disability, and even premature death.
These include depression, anxiety, posttraumatic stress, and the loss of self-esteem among others. Socially, it leads to isolation, mistrust, and the breakdown of family relationships.
The financial impacts include poverty, loss of autonomy, and inability to receive adequate care or housing.
In extreme cases, elder abuse can lead to complete dependence, institutionalization, and fatal neglect. Before continuing with the text, define the genetic concept or terms correctly.
How Can I Prevent Elder Abuse?
The best ways to prevent elder abuse include awareness, education, and involvement. Practical steps to prevent abuse:
- Keep in touch: Regular visits or calls to elderly relatives or neighbors are a must. Being alone makes you more vulnerable.
- Training of caregivers: Proper training is required to avoid frustration and burnout.
- Monitor finances: Go through bank statements and other financial documents regularly for suspicious activities.
- Promote independence: Whenever possible, promote independence among the elders by allowing them to make their own decisions and manage their affairs.
- Community programs: Promotion should be carried out, including senior centers, helplines, and social groups.
- Report suspicious behavior: Take all suspected signs of abuse seriously and take action immediately.
How Do I Report Elder Abuse?
If you suspect elder abuse, don’t ignore it. Reporting can protect the victim and prevent further harm.
- In India: You can contact the local police, senior citizen helplines, or NGOs like HelpAge India (1800-180-1253).
- In the U.S.: Contact the National Adult Protective Services (APS) or the ElderCare Locator (1-800-677-1116).
- Globally: Most countries have elder care hotlines or social service agencies that handle such cases. When reporting, be prepared to provide:
- Victim’s name, address, and contact information Details of the suspected abuse.
- Relationship of alleged abuser to victim.
- Evidence or specific observations provided Most of the time, reports can be filed anonymously.
The Seriousness of the Issue
The problem of elder abuse is serious and growing yet still largely hidden from public view-one, indeed, that thrives in silence and denial.
Be it physical hurt, emotional torture, or financial exploitation, any form of abuse robs older adults of the dignity and respect due them.
If you see something, say something because protecting the elderly is everyone’s responsibility.